Binary Tree in Python
Last updated on March 12, 2023 am
Binary Tree in Python
Definition
A binary tree might be the simplest tree data structure. It only have three attributes: the value of the node, its left and right child node. If its child node is None, this child node do not have value or child nodes anymore.
Here is the definition of a typical binary tree from LeetCode:
1 | |
Similar to linked list, binary tree is also a one direction data type. Once moved to its child node, there is no way to trace back, except going through it from the head node again.
In LeetCode, the input is a list-like binary tree, which is probably difficult to understand at the first glance. For example, inputs wirtten as [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15] and [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, null, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12] should be interpretered as image below.
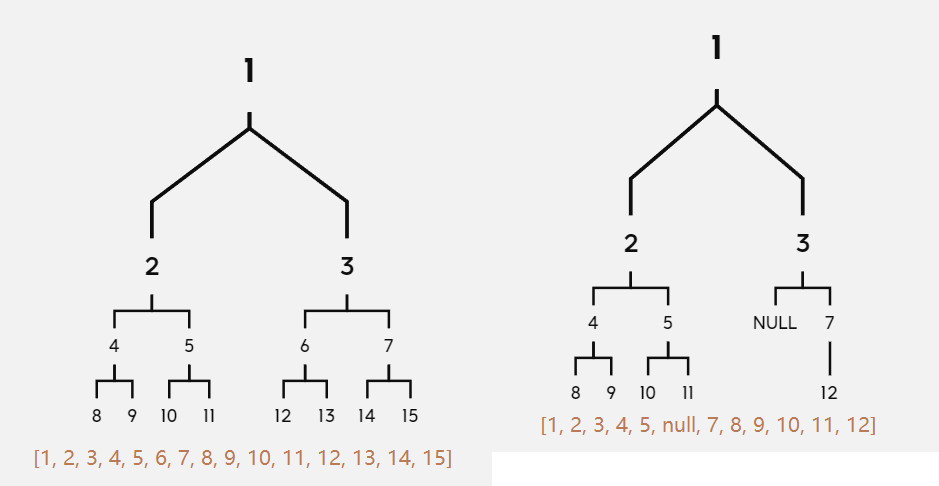
It is not extremely significant, however, since we just need to cope with its attributes in our implementation.
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Easy)
This problem is really a great intro to the understandment of binary tree. It require atraversal of given binary tree.
By inspecting the output, it should be implemented in depth first search (DFS), with left child node searched first. This sounds like nonsense as the input is given layer by layer. But this really confused me at very first.
Unquestionably, this problem could be solved by recursion.
1 | |
Don’t need to worry about what if it’s left or right attribute is null, it would pass in next function call.
Some Similar Questions
Same Tree
We can apply similar logic to the question 100. Same Tree (Easy).
1 | |
Symmetric Tree
And the question 101. Symmetric Tree (Easy).
1 | |
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (Easy)
1 | |
Recursion is probably the simplist way to manage a binary tree, and there is no waste on calculating same base cases.
Balanced Binary Tree
110. Balanced Binary Tree (Easy)
1 | |
Here, for the first time, comes some waste calculation.